How to operate a drone is a question many ask, and the answer encompasses far more than simply grasping a controller. It’s about understanding the technology, respecting regulations, and appreciating the potential for stunning aerial photography and videography. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to confidently navigate the world of drone piloting, from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques.
From mastering basic controls and understanding flight modes to capturing breathtaking aerial shots and ensuring responsible operation, we’ll cover everything you need to know. We’ll also delve into essential maintenance, legal considerations, and the use of drone software and applications. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive guide will serve as your trusted companion in the exciting world of drone operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, and potential harm to people or property. This section details a comprehensive checklist and safe launch/landing procedures.
Pre-Flight Inspections: Importance and Checklist
Pre-flight inspections are paramount for identifying potential issues before takeoff. A quick visual inspection can prevent costly repairs or accidents. This involves checking the drone’s physical condition, battery status, and GPS signal strength.
- Battery Check: Verify battery level and ensure it’s securely connected. Check for any signs of damage, swelling, or leaks.
- Propeller Inspection: Examine each propeller for cracks, bends, or damage. Ensure they are securely fastened.
- GPS Signal Verification: Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. The number of satellites acquired should be sufficient for stable flight.
- Gimbal Check (if applicable): Verify the gimbal is functioning correctly and is securely mounted.
- Camera Check (if applicable): Ensure the camera is clean and functioning correctly. Check lens for smudges or obstructions.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone for any damage or loose components.
Safe Drone Launch and Landing Procedure
Launching and landing a drone safely requires a methodical approach. The following steps minimize the risk of accidents.
- Choose a Safe Location: Select a location away from obstacles, people, and airspace restrictions.
- Power On: Power on the drone’s remote controller first, followed by the drone itself.
- Calibration (if necessary): Calibrate the compass and IMU sensors as per the drone’s manual.
- Pre-Flight Checks: Perform the pre-flight checklist Artikeld above.
- Gentle Ascent: Initiate a slow and controlled ascent, keeping a close eye on the drone’s altitude and surroundings.
- Controlled Descent: For landing, initiate a slow and controlled descent, maintaining visual contact with the drone until it touches down.
- Power Off: Power off the drone first, followed by the remote controller.
Drone Battery Comparison
Different drone batteries offer varying flight times and weights. The choice depends on mission requirements and drone capabilities.
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Flight Time (approx.) | Weight (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S 1500mAh | 1500 | 15-20 minutes | 150g |
| LiPo 4S 2200mAh | 2200 | 25-30 minutes | 220g |
| LiHV 4S 3000mAh | 3000 | 35-40 minutes | 280g |
| LiFePO4 6S 5000mAh | 5000 | 45-50 minutes | 400g |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective operation. This section covers basic controls, flight modes, and maneuvering techniques.
Basic Drone Controls
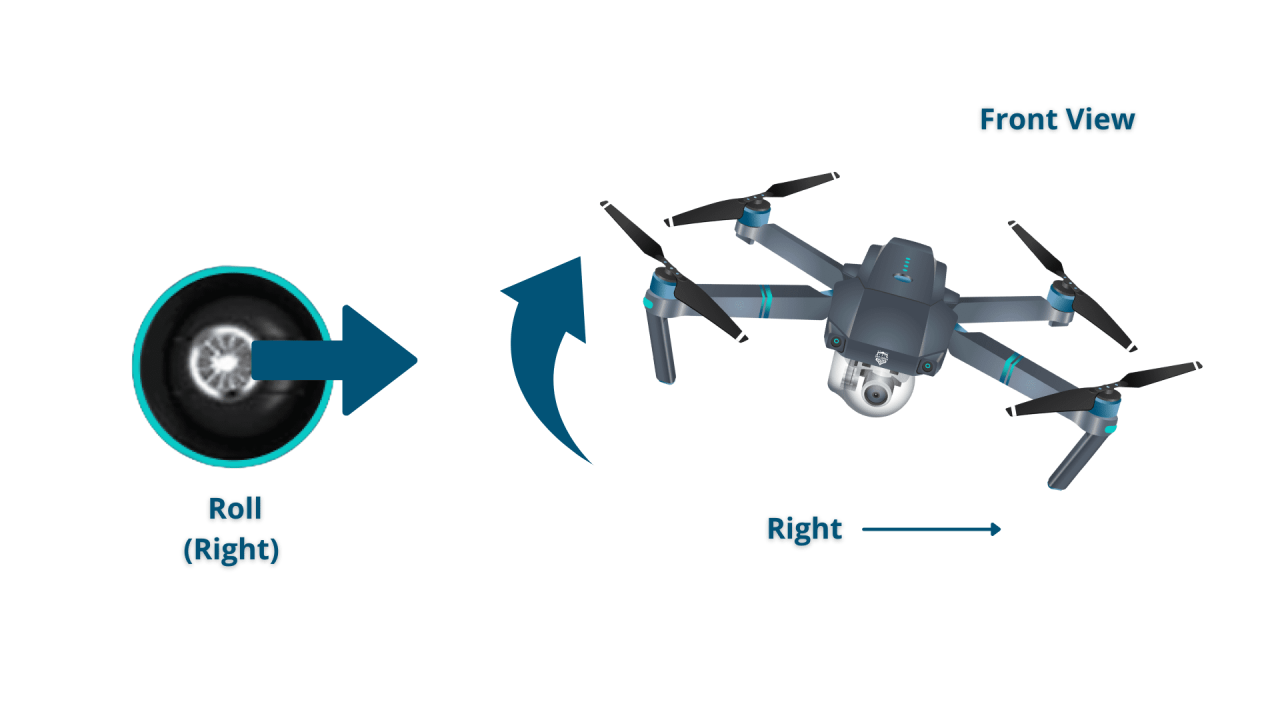
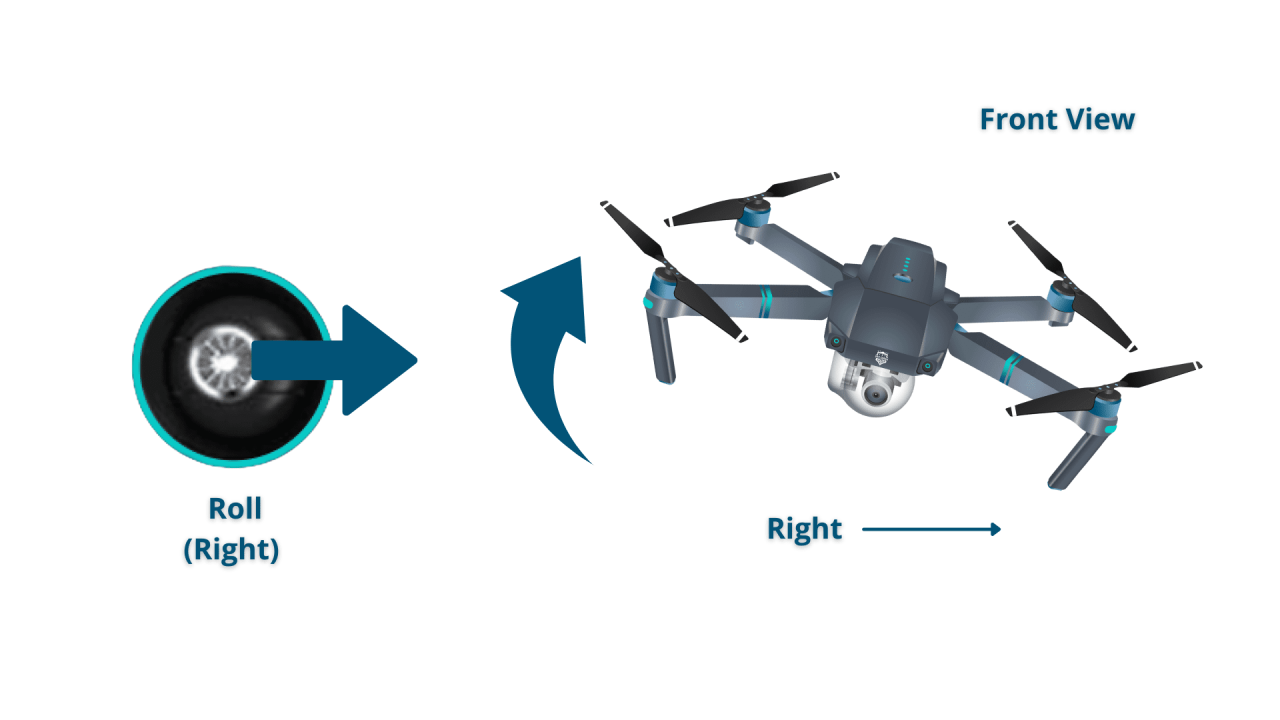
Most drones use two joysticks for primary control. One joystick controls the drone’s altitude and direction, while the other controls its yaw (rotation) and movement.
The left joystick typically controls altitude and direction. Pushing it forward increases speed in the direction the drone is facing, while pushing it backward decreases speed or moves it in reverse. Moving the joystick left or right causes the drone to move laterally.
The right joystick typically controls the yaw (rotation) and horizontal movement. Pushing it left or right causes the drone to rotate. Pushing it forward or backward often adds an element of lateral movement to the drone’s movement, adding to its overall trajectory.
Additional buttons and switches control functions like camera tilt, return-to-home, and emergency stops.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and autonomy. Understanding these modes is critical for safe and efficient flight.
- Attitude Mode: The drone’s orientation remains relative to the pilot’s perspective. Moving a joystick moves the drone relative to its current orientation.
- GPS Mode: The drone maintains its position using GPS, providing more stability and ease of use, especially for beginners.
- Return to Home (RTH): This automated function returns the drone to its takeoff point.
- Sport Mode (if applicable): This mode increases the responsiveness and speed of the drone, suitable for experienced pilots.
Smooth and Controlled Drone Maneuvers
Smooth and controlled maneuvers are essential for capturing high-quality footage and preventing accidents.
- Use Smooth Joystick Movements: Avoid abrupt movements to prevent jerky footage and maintain stability.
- Maintain a Safe Altitude: Keep the drone at a safe altitude to avoid obstacles and maintain a clear line of sight.
- Practice in Open Spaces: Practice flying in open areas before attempting complex maneuvers in confined spaces.
- Use Flight Simulation Software: Practice using flight simulators to hone your skills before flying a real drone.
Navigating to a Specific GPS Coordinate
Many drone apps allow you to input GPS coordinates to navigate the drone to a specific location.

The flowchart would visually represent steps such as entering GPS coordinates in the app, initiating the flight plan, monitoring the drone’s progress, and making adjustments as needed.
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos: How To Operate A Drone
Capturing stunning aerial imagery requires understanding factors influencing image quality and employing effective camera settings and flight techniques.
Factors Influencing Image Quality

Several factors contribute to the quality of aerial photos and videos. These include lighting conditions, camera settings, and drone stability.
- Lighting: The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) offers soft, diffused light ideal for photography and videography. Avoid harsh midday sun.
- Camera Settings: Proper exposure, ISO, shutter speed, and aperture settings are crucial for optimal image quality.
- Drone Stability: A stable platform is essential for sharp, blur-free images and smooth video footage. Wind can significantly impact stability.
Camera Settings Adjustments for Various Shooting Scenarios
Adjusting camera settings optimizes image quality based on the shooting scenario.
- Landscape: Wide angle lens, lower ISO, slower shutter speed for sharp details.
- Portrait: Telephoto lens (if available), adjust aperture for desired depth of field.
- Close-up: Higher shutter speed to freeze motion, potentially higher ISO if lighting is low.
Achieving Smooth, Cinematic Drone Footage

Smooth, cinematic footage requires careful flight techniques and post-processing.
- Smooth, controlled movements: Avoid jerky movements by using gentle joystick inputs.
- Consistent altitude and speed: Maintain consistent altitude and speed for smoother transitions.
- Use of cinematic flight modes: Explore cinematic flight modes available in your drone’s app.
- Post-processing: Utilize video editing software to refine footage and enhance its cinematic quality.
Composing Visually Appealing Aerial Shots
Effective composition enhances the visual impact of aerial photography and videography.
- Rule of thirds: Place key elements along the imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds.
- Leading lines: Use roads, rivers, or other lines to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Symmetry and patterns: Capture symmetrical scenes or repeating patterns for visually interesting shots.
- Framing: Use natural elements, like trees or buildings, to frame your subject.
- Perspective: Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create unique shots.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are vital for prolonging the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued reliable performance.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Several issues can arise during drone operation. Identifying the cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
- Low Battery: Insufficient battery power can lead to unexpected power-offs mid-flight.
- GPS Signal Loss: Interference or weak signals can affect the drone’s stability and positioning.
- Propeller Damage: Damaged propellers can cause vibrations and unstable flight.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Problems with the gimbal can affect camera stability and image quality.
- Sensor Errors: Faulty sensors can lead to inaccurate readings and erratic flight behavior.
Cleaning and Maintaining Drone Components
Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial for preserving the drone’s performance and longevity.
- Propeller Cleaning: Gently clean propellers with a soft cloth and mild soap to remove dirt and debris.
- Camera Cleaning: Clean the camera lens with a microfiber cloth to prevent smudges and scratches.
- Body Cleaning: Wipe the drone body with a damp cloth to remove dirt and dust.
- Inspecting for Damage: Regularly inspect the drone for any signs of damage or wear and tear.
Regular Battery Care and Storage
Proper battery care extends battery life and ensures safety.
- Avoid Overcharging: Avoid overcharging the battery, as this can damage it.
- Store at Moderate Temperatures: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Do not expose batteries to extreme temperatures, as this can affect their performance.
- Proper Storage: Store batteries at a moderate charge level (around 30-50%) when not in use for extended periods.
Common Problems and Solutions
This table lists common problems and their solutions.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Check battery connection and charge level. |
| GPS signal lost | Move to an area with better GPS reception. |
| Drone is unstable | Check propellers for damage. Calibrate the IMU. |
| Camera not functioning | Check camera settings and connections. |
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to legal regulations and ethical guidelines.
Relevant Regulations and Laws
Drone regulations vary by region. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific laws in your area before flying.
These laws often cover aspects like registration, licensing, permitted airspace, and operational restrictions near airports or sensitive areas. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines or legal consequences.
Ethical Implications of Drone Usage
Responsible drone operation involves respecting privacy and avoiding any actions that could be considered intrusive or harmful.
- Privacy: Avoid filming people without their consent. Be mindful of where you are flying and what you are capturing.
- Responsible Flying: Fly safely and responsibly, avoiding any actions that could endanger others or property.
- Respecting Airspace Restrictions: Adhere to all airspace restrictions, including those near airports and other sensitive areas.
Scenarios Where Drone Operation is Restricted or Prohibited
Several scenarios restrict or prohibit drone operation.
- Near airports or military bases: Drones are typically prohibited from flying near airports and military bases without special permission.
- Overcrowded areas: Flying drones over large crowds can be dangerous and may be illegal.
- Private property: Unless you have permission from the property owner, you should not fly a drone over private property.
- National parks or protected areas: Certain national parks and protected areas may have restrictions or prohibitions on drone use.
Best Practices for Safe and Responsible Drone Operation
Following these best practices ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
- Always maintain visual line of sight: Keep your drone within your visual range at all times.
- Check weather conditions before flying: Avoid flying in windy or stormy conditions.
- Respect privacy: Avoid filming people without their consent.
- Adhere to local laws and regulations: Ensure your drone operation complies with all relevant laws.
- Fly responsibly: Avoid reckless or dangerous flying practices.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced techniques for more complex drone operations and high-quality aerial captures.
Planning Complex Drone Flights Using Flight Planning Software
Flight planning software allows pilots to pre-program complex flight paths, including waypoints, altitude changes, and camera movements. This is crucial for capturing cinematic shots or conducting inspections that require precise movements.
Software such as Litchi, DroneDeploy, and Pix4Dcapture offer features like obstacle avoidance, automated flight paths, and integration with various drone models. These tools allow for more efficient and safer operation, especially in challenging environments or for complex aerial photography projects.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and a thorough understanding of its controls; for a comprehensive guide, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on consistent practice and adherence to safety guidelines.
Achieving Stable Shots in Windy Conditions
Wind can significantly impact drone stability. Techniques to mitigate this include using heavier batteries (within the drone’s limits), adjusting flight settings to reduce sensitivity to wind, and choosing calmer times for flights.
Understanding wind patterns and adjusting flight paths accordingly is crucial for maintaining stability. Flying in sheltered areas can also significantly reduce the impact of wind on drone performance.
Advanced Camera Settings and Features, How to operate a drone
Advanced camera settings allow for greater control over image quality and creative expression.
- Aperture: Controls depth of field, influencing background blur.
- Shutter Speed: Affects motion blur and exposure.
- ISO: Controls sensitivity to light, impacting image noise.
- White Balance: Adjusts color temperature for accurate color reproduction.
Performing a Drone Flip or Other Advanced Maneuver
Advanced maneuvers like flips require significant practice and skill. These should only be attempted in open, safe spaces, away from obstacles and people, after mastering basic controls.
Many drones offer specific modes or settings for advanced maneuvers. It’s essential to carefully read the drone’s manual and understand the risks involved before attempting these techniques.
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical skill, responsible awareness, and creative vision. Mastering the fundamentals, as Artikeld in this guide, provides a strong foundation for safe and effective flight. Remember, consistent practice, a respect for regulations, and a commitment to ethical operation will elevate your drone piloting experience and unlock the full potential of this innovative technology.
Embrace the skies responsibly, and enjoy the journey!
General Inquiries
What is the minimum age to operate a drone?
Drone operation age restrictions vary by region and drone class. Check your local aviation authority’s regulations.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if you’ve moved significantly or experienced interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If GPS signal is lost, immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, perform a controlled landing.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the proper control techniques, and for detailed guidance on this, you should consult a comprehensive resource such as this guide on how to operate a drone. Safe and effective drone operation requires practice and a thorough understanding of its functionalities; familiarizing yourself with these aspects is essential for responsible flying.
Can I fly my drone in bad weather?
No. Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, snow, or fog. Adverse weather conditions significantly reduce visibility and control.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements differ based on location. Consult your local aviation authority for specific regulations.